Prokopp Residence – LEED Silver – Lake Angelus, MI
/0 Comments/in Local, -local, Certified Homes, Certified LEED, Green Home Institute, LEED Silver, Michigan, Project Profile/by Brett LittleNewland Residence is Greenstar Gold Certified
/0 Comments/in Local, Certified Homes, Certified LEED, GreenStar, GS Gold, LEED Silver, Minnesota, Project Type, Single-Family Projects/by Brett LittleWhole Foods Mixed Use Market Rate Housing Certify LEED Silver in Minneapolis
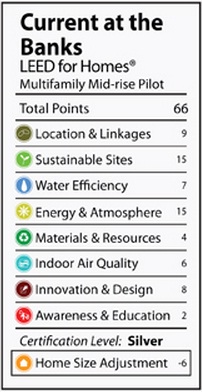
/0 Comments/in LEED Midrise, LEED Silver, Minnesota, Multi-Family Projects/by Brett LittleRyan Companies and The Excelsior Group collaborated to bring this 579,706-square-foot mixed-use project to downtown Minneapolis. The project – called 222 Hennepin – will contain 286 luxury apartments and will be anchored by the first Whole Foods Market in downtown Minneapolis.

Ryan Companies co-developed the project with The Excelsior Group, specialists in multifamily real estate. Ryan is also the architect-of-record and builder for the project, which will occupy a full city block at the corner of Hennepin and Washington Avenues. The corner is one of the most prominent downtown, and development challenges had kept it vacant for more than five years.
A 40,000 -square-foot Whole Foods Market occupies the ground floor of the project. Luxury apartments, featuring dramatic views of the downtown skyline and Mississippi River, occupy the second through sixth floors. Ryan Design worked with Humphreys & Partners Architects on the conceptual design of the project, which focused on balancing the housing needs of sophisticated, discerning apartment residents with the commercial needs of a top-tier urban grocery store.
 Project amenities include a fourth-floor terrace with an outdoor pool, bocce ball area, fire pit, dog walk, enclosed party room, cyber cafe and state-of-the-art fitness center. The terrace itself affords spectacular views of the downtown Minneapolis skyline. The construction of the project prioritizes sustainable building practices by incorporating an existing 300-stall parking structure, effectively wrapping the new project around the existing improvements and re-using them.
Project amenities include a fourth-floor terrace with an outdoor pool, bocce ball area, fire pit, dog walk, enclosed party room, cyber cafe and state-of-the-art fitness center. The terrace itself affords spectacular views of the downtown Minneapolis skyline. The construction of the project prioritizes sustainable building practices by incorporating an existing 300-stall parking structure, effectively wrapping the new project around the existing improvements and re-using them.
In working toward LEED Silver Certification for mid-rise residential, the team
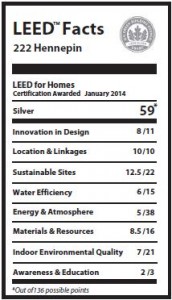 incorporated a variety of sustainable and energy-saving elements into the new building. Some of these features include:
incorporated a variety of sustainable and energy-saving elements into the new building. Some of these features include:
- The downtown location encourages the use of public transportation as well as bike and foot traffic, which reduces emissions. In addition, the compact, amenity-rich site promotes community living.
- The existing 300-stall parking structure remained in place, which saved in excess of 20 million pounds of concrete and over 1 million pounds of steel rebar that would have been used to replace it.
- Saving the existing parking structure drastically reduced the demolition waste that would have been generated.
- Cleaning up, reinvesting and redeveloping an urban brownfield site of contaminates protects the environment and reduces blight.
- The building is 100% smoke-free and extra measures have been taken to seal the units to reduce air leakage which will lower the risks of indoor air pollutants.
- The use of high efficiency water faucets, showers and toilets reduce water demand.
- The off-site fabrication of the interior roof, walls and floors minimized the waste created on-site. In addition, approximately 65% of the construction waste was diverted from landfills through recycling programs.
- The use of low maintenance, non-invasive native plants, which will thrive in an urban environment, will reduce irrigation needs.

Click here to learn more about Ryan’s sustainability efforts.
Follow 222 Hennepin on Facebook or Twitter for the latest project updates.
Awards
- National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) 2013 Best In American Living Awards (BALA), Silver Award for On the Boards, Multifamily
- Minneapolis/St. Paul Business Journal 2013 Best in Real Estate, Best Overall and Best Mixed-use Urban Awards
- Pacific Coast Builders Conference (PCBC) 2013 Golden Nugget Award, Best On-the Boards Mixed Use Project
– http://www.ryancompanies.com/projects/222-hennepin/
South east MI home scores LEED silver and is a top energy performer
/0 Comments/in Local, LEED Silver, Michigan, Single-Family Projects/by Brett LittleThis newly constructed LEED Silver Home is located on the north side of Ann Arbor, on a 5 acre lot. The home is 4,500 square feet with 6 bedrooms, 2 ½ baths, and has a walk-out basement.
 The project team wanted to build a very energy efficient, comfortable home for the family to raise their children in. Throughout the project, the team emphasized purchasing sustainable materials including adhesives and sealants with zero Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC’s) to attain a higher air quality. They worked with a HERS rater to hone in on their energy efficiency strategies. Northern Michigan Oak hardwood flooring was used throughout the first floor of the home because of its close proximity to the project. All carpeting and underlayment were Green Label Plus certified by the GreenGuard Certification Institute. Blown-in cellulose insulation, which is made up of 100% recycled newspaper fiber, was used instead of fiberglass. The fitness room boasts a 100% recycled rubber flooring and the TREX deck had a high percentage of recycled materials as well. A drought resistant turf grass mix limited irrigation requirements, as well as a wildflower mix on the perimeter of the turfed-in area. Additionally, only native species of bushes and trees were installed. The system is controlled by a RainBird Sensor that automatically adjusts the irrigation schedules if it senses rainfall.
The project team wanted to build a very energy efficient, comfortable home for the family to raise their children in. Throughout the project, the team emphasized purchasing sustainable materials including adhesives and sealants with zero Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC’s) to attain a higher air quality. They worked with a HERS rater to hone in on their energy efficiency strategies. Northern Michigan Oak hardwood flooring was used throughout the first floor of the home because of its close proximity to the project. All carpeting and underlayment were Green Label Plus certified by the GreenGuard Certification Institute. Blown-in cellulose insulation, which is made up of 100% recycled newspaper fiber, was used instead of fiberglass. The fitness room boasts a 100% recycled rubber flooring and the TREX deck had a high percentage of recycled materials as well. A drought resistant turf grass mix limited irrigation requirements, as well as a wildflower mix on the perimeter of the turfed-in area. Additionally, only native species of bushes and trees were installed. The system is controlled by a RainBird Sensor that automatically adjusts the irrigation schedules if it senses rainfall.
 A Home Energy Rating Standard (HERS) Score of 44 was achieved for this house, which makes it in the top 10% of MI homes. The score means that the home is 56% more efficient than a conventionally built new home, and 42% more efficient than Energy Star’s standard for homes. To give you an understanding of what this equates to, the energy bill for this 4,500 sq. ft home during the month of July, was $110 for both electric and gas. The project team chose to focus on the Energy & Atmosphere and Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) credit areas to compensate for the sacrifice of Location & Linkages credits due to the projects distance from an urban setting. The high rating of LEED Silver was achieved by taking a whole systems design approach to building, and eliminating any weak points in the house.
A Home Energy Rating Standard (HERS) Score of 44 was achieved for this house, which makes it in the top 10% of MI homes. The score means that the home is 56% more efficient than a conventionally built new home, and 42% more efficient than Energy Star’s standard for homes. To give you an understanding of what this equates to, the energy bill for this 4,500 sq. ft home during the month of July, was $110 for both electric and gas. The project team chose to focus on the Energy & Atmosphere and Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) credit areas to compensate for the sacrifice of Location & Linkages credits due to the projects distance from an urban setting. The high rating of LEED Silver was achieved by taking a whole systems design approach to building, and eliminating any weak points in the house.
Mixed Use Midrise LEED Certified Silver In Cincinnati
/0 Comments/in Local, LEED Midrise, LEED Silver, Ohio/by Brett LittleWebinar: Post Occupancy Study – LEED for Homes on Affordable Housing
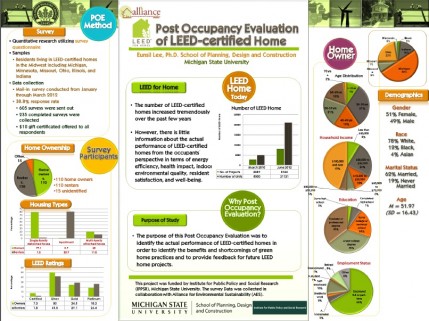
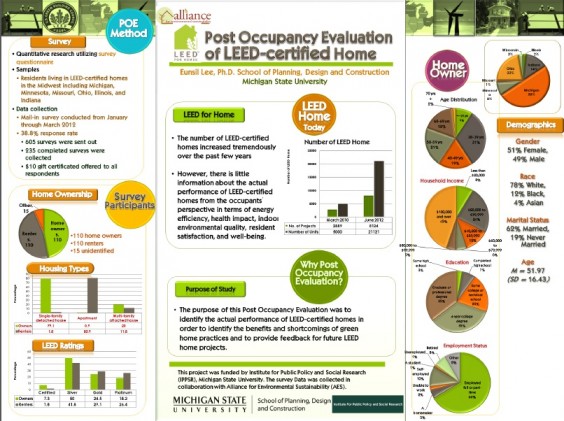
/0 Comments/in Economics, Illinois, Indiana, LEED Certified, LEED Gold, LEED Platinum, LEED Silver, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Tools and Resources, Wisconsin/by Brett Littlerecently partnered with Michigan State University (MSU) to perform a Post-Occupancy Evaluation (POE) of 235 LEED-certified homes in the Midwest, and we are pleased to share the results. The goal is to identify the homes’ actual performance after people moved in, and also the
benefits and shortcomings of the current LEED for Home certification system. The survey consisted of various categories including (1) general satisfaction with the LEED-certified home, (2) satisfaction about the home in general and various aspects of the indoor environment, (3) overall well-being including the health impact, (4) energy efficiency and building performance, (5) the environmental behavior of residents, and (6) demographics.
The findings of this study revealed that most residents of the LEED-certified home were satisfied with their home and their quality of life in their home.
Continuing Education
- 1 GBCI – General
- 1 MI Contractor (Code & Green)
- 1 MI Architect
- If you need continuing education units for a license in another state, this course may apply. Please consult your state’s requirements.
This webinar is free to review. If you are interested in continuing education credits, you must follow the following steps:
1. Watch the webinar presentation by Eunsil Lee, PhD for FREE.
2. Contact to take the quiz and score at least 80% to be approved. Please also post a comment below and help add to the conversation.
3. Pay the fee below to get your certificate and CEUs. You must be an member to pay the reduced member fee.
Two methodological approaches were used for this study. Qualitative case studies were conducted with 15 LEED-certified Habitat for Humanity residents in Kent County, Michigan through in-depth interviews, observations, and IEQ measurement. 16 % respondents came from LEED-certified Habitat for Humanity homes in Michigan. These residents in particular, were more satisfied with their homes and their quality of life than residents of Non- Habitat homes were, although their satisfaction with their neighborhood and specific aspects of home environment (e.g., space layout, size of space, finishes, visual privacy, view, temperature, humidity) was lower than that of Non-Habitat residents. Residents of the Habitat for Humanity tended to perceive the improvement of their quality of life since moving into their LEED-certified home more strongly than residents of the Non-Habitat home did. They were also more satisfied with energy efficiency of their home than residents of the Non-Habitat home.
2 page graphic summary of Study PDF Here
Full 96 Page Report on Post Occupancy Study
Report Recommendations:
Promote sustainability in low-income housing: More programs should be developed that can offer incentives for participation in LEED green building certification programs and increase funding opportunities to cover the initial costs of sustainable home building for low-income families at both state and local levels, because those efforts will produce long-term economic and environmental benefits.
Improve the design of low-income green housing: Architects, designers, engineers, contractors, and facility managers can gain greater understanding of design and the performance of low-income green homes with the findings of this POE project by receiving feedback for the future projects. Although the houses were LEED-certified, some problems in maintaining the green features, building performance, and comfortable home environment were identified. Architects, designers, engineers, green policy makers, and Habitat for Humanity Affiliates should pay attention to the specific needs relevant to these issues to improve the design quality of low-income green home through the process of planning, design, and construction.
Implement Post-Occupancy Evaluation (POE): More extensive implementation of POEs is critical. Since LEED certification is based on “as-designed” performance, further implementation of POEs is exceptionally important to verify actual performance and expected performance. In particular, since there is no mandatory post-occupancy evaluation process included in LEED or other green home certifications, there is no empirical data to verify whether these green homes perform satisfactorily in terms of heating, cooling, or indoor environmental quality.
Contribute to the general body of knowledge: Although there is a consensus about the benefits of green homes, few empirical studies about the actual effects of LEED-certified green homes on residents’ health, comfort, and satisfaction have been conducted. The findings from this study therefore increased understanding of the benefits to be gained from LEED-certified low-income homes by applying empirically tested, research -based knowledge.
Promote public awareness: This report will educate the public about the impact of LEED-certified homes on (1) improving the residential environmental quality and energy efficiency, (2) reducing residents’ health risks and (3) enhancing residents’ comfort and satisfaction by disseminating the results of this research at conferences and by publishing articles in scholarly and extension journals.
Make a Policy Recommendation:
1) Incentives for green homes, such as LEED-certified homes, Energy Star Homes, or National Association of Home Builders’ Green certified homes, should be offered to developers, contractors, and homeowners. This will be critical for both new and existing homes located in the cold regions such as Michigan to encourage energy-efficient green home constructions for low-income families in order to offer lower utility bills.
2) Policy makers should collaborate closely with local builders and developers to apply more green home features to new or existing low-income houses. Certain types of incentives for local builders and developers are desired.
3) Post-occupancy evaluations of green certified homes should be encouraged, particularly for low-income housing. Continuous efforts should be made to save energy and keep green homes energy-efficient for these households and homeowners.
4) We suggest conducting POEs of green certified homes in five or ten years to preserve their green features and energy efficiency. Based on the POEs, the homes may or may not be repaired to keep the original functions of green features. In the POEs and repairing process, local home remodeling companies can be involved. Some incentives should be considered for the local companies or businesses to be involved in this green process if they are small or micro businesses. Tax reductions for these types of companies (i.e., energy auditors, window replacement companies) can promote small entrepreneurs working on sustainable housing projects in local communities. This can create more local jobs.
5) We suggest offering regular educational seminars for residents of green certified homes in order to offer precise information about the green features of their homes and educate them how to keep their homes green. On-site seminars can be offered one or two times in the development phase and right before the new owners take occupancy. Once residents move to their new homes, it is recommended to send flyers via mail or email to remind them of the green features of their homes and inform them of how to use and maintain these features. Mailed or emailed flyers will work better than on-site seminars because many residents have full- or part-time jobs.
6) In addition, incentives should be considered for upgrading low-income housing to make it more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Currently there is a 500 dollar maximum tax credit for upgrading any housing features to make them energy-efficient. This maximum should be increased to keep up with the real cost of upgrading energy-consuming HVAC systems to energy-efficient ones. In particular, more aggressive incentives should be offered to households below a certain income level so that homeowners can be more active in upgrading their conventional houses to energy-efficient green ones.
Thanks to the Michigan Applied Public Policy Research (MAPPR) Grant from the Institute for Public Policy and Social Research (IPPSR) and Michigan State University (MSU) who worked with to perform this Post-Occupancy Evaluation (POE).
See more details on a similar LEED Pre-Occupancy Report.
Cottage Home Sets New Standard for Sustainable Lakefront Living
/0 Comments/in Certified Homes, Illinois, Indiana, LEED Certified, LEED Gold, LEED Platinum, LEED Silver, Michigan, Single-Family Projects/by Brett LittleUsing his home building expertise, Brian Bosgraaf started Cottage Home in 2000 specializing in building custom homes along Lake Michigan. Cottage Home has designed and built more than 70 custom homes along the West Michigan shoreline, including 13 LEED certified homes. In an interview with Brian, he expressed his passion for LEED certification and sustainable construction practices.
 When Brian and Jeremy vanEyk (Vice President) were asked about their commitment to building LEED, they responded that Cottage Home is committed to utilizing healthy, affordable, efficient, and durable construction practices that are already above code, energy star and even LEED at times. Brian says he considers LEED only one of the many tools in his toolbox. Other such tools include creative design, customer service, careful selection of materials, and creating a sense of place. In order to make it simple for the customer, Cottage Home uses a fixed price prior to starting construction which already includes LEED qualifications. This allows some of the cost of LEED certification to be absorbed by both the customer and through the Cottage Homes marketing budget. Brian believes this method works due to his design and construction teams working together throughout the construction process, which creates a feedback loop that fosters constant improvement. Including LEED certification into the final cost helps facilitate more sales than presenting each option with separate pricing.
When Brian and Jeremy vanEyk (Vice President) were asked about their commitment to building LEED, they responded that Cottage Home is committed to utilizing healthy, affordable, efficient, and durable construction practices that are already above code, energy star and even LEED at times. Brian says he considers LEED only one of the many tools in his toolbox. Other such tools include creative design, customer service, careful selection of materials, and creating a sense of place. In order to make it simple for the customer, Cottage Home uses a fixed price prior to starting construction which already includes LEED qualifications. This allows some of the cost of LEED certification to be absorbed by both the customer and through the Cottage Homes marketing budget. Brian believes this method works due to his design and construction teams working together throughout the construction process, which creates a feedback loop that fosters constant improvement. Including LEED certification into the final cost helps facilitate more sales than presenting each option with separate pricing.
 Since many homeowners today are educated and concerned about sustainability and environmental issues, many take time to study the details of LEED on the website of Cottage Home and take comfort in knowing LEED is a third party certification. Clients are aware of LEED’s achievements and credibility, and often wonder about how changes to the house affect the LEED certification level. Much of Cottage Home’s customer base is from the Chicago area where LEED is prevalent in their office buildings, and a result, many clients have experienced the advantages offered by LEED construction firsthand. These clients have often already invested in commercial LEED projects and are now ready to transition these same high standards to their personal lives. Jeremy decided to experience the benefits of LEED firsthand and chose to have his own house in Zeeland, certified LEED Platinum.
Since many homeowners today are educated and concerned about sustainability and environmental issues, many take time to study the details of LEED on the website of Cottage Home and take comfort in knowing LEED is a third party certification. Clients are aware of LEED’s achievements and credibility, and often wonder about how changes to the house affect the LEED certification level. Much of Cottage Home’s customer base is from the Chicago area where LEED is prevalent in their office buildings, and a result, many clients have experienced the advantages offered by LEED construction firsthand. These clients have often already invested in commercial LEED projects and are now ready to transition these same high standards to their personal lives. Jeremy decided to experience the benefits of LEED firsthand and chose to have his own house in Zeeland, certified LEED Platinum.
 Building on the lake front comes with complications such as extreme wind loads, humid changes, temperature fluctuation, and other variables. To overcome these challenges, Cottage Home uses high performance home measures to control the entire process though design, build, and some maintenance which allows more control of green features. Cottage Home designs and builds what is right for each particular home which may result in homes varying in different HVAC, insulation, passive solar heating, and various climate control systems. One particular feature that is commonly used in these homes, including Jeremys, is an ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilator). An ERV automatically exhausts stale air from the inside of the house and replaces it with fresh air from the outside. Another key feature used in many of the homes is a geothermal system. There are a few different types used, but all contribute to the energy efficiency of the homes in some way. Several techniques are used to increase water efficiency in the homes, such as tankless water heaters, which only heat water when necessary, water collection systems to help with sprinking and irrigation, and faucets and showerheads that work with less water than traditional ones. Insulation, as well as materials such as flooring, home furnishings and walls are all aspects that need to be carefully considered when building these homes.
Building on the lake front comes with complications such as extreme wind loads, humid changes, temperature fluctuation, and other variables. To overcome these challenges, Cottage Home uses high performance home measures to control the entire process though design, build, and some maintenance which allows more control of green features. Cottage Home designs and builds what is right for each particular home which may result in homes varying in different HVAC, insulation, passive solar heating, and various climate control systems. One particular feature that is commonly used in these homes, including Jeremys, is an ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilator). An ERV automatically exhausts stale air from the inside of the house and replaces it with fresh air from the outside. Another key feature used in many of the homes is a geothermal system. There are a few different types used, but all contribute to the energy efficiency of the homes in some way. Several techniques are used to increase water efficiency in the homes, such as tankless water heaters, which only heat water when necessary, water collection systems to help with sprinking and irrigation, and faucets and showerheads that work with less water than traditional ones. Insulation, as well as materials such as flooring, home furnishings and walls are all aspects that need to be carefully considered when building these homes.
 As leaders in the industry we asked Brian and Jeremy what they saw in the future of design and construction. Jeremy believes that being able to evaluate the effectiveness of high performance systems and insulation through energy bills is important. Along with water collection systems to reduce storm water runoff and help irrigate the lawn. Brian agrees that we should have a system to allow clients to ensure they are getting the most effective homes. He foresees homes that can be manipulated to meet the client’s needs at any given time. An example of this would be homes with the ability to accommodate a family of four, which can then transition to accommodate sleeping arrangements for twenty. Along with being able to better meet a client’s needs, he would like to see energy loads distributed to only sections of the house in use, as well as the ability for clients to control how energy is used throughout the home (on site and from satellite locations). Cottage Home sees one challenge to moving forward with these ideas is getting sub-contractors to approach basic air sealing, insulation, proper HVAC sizing, and design aesthetics with an effective mindset. Cottage Home has established themselves as innovators and leaders in the design of luxury LEED lake front homes. They continue to partner quality, design and the environment hand in hand to produce sustainability along our beaches.
As leaders in the industry we asked Brian and Jeremy what they saw in the future of design and construction. Jeremy believes that being able to evaluate the effectiveness of high performance systems and insulation through energy bills is important. Along with water collection systems to reduce storm water runoff and help irrigate the lawn. Brian agrees that we should have a system to allow clients to ensure they are getting the most effective homes. He foresees homes that can be manipulated to meet the client’s needs at any given time. An example of this would be homes with the ability to accommodate a family of four, which can then transition to accommodate sleeping arrangements for twenty. Along with being able to better meet a client’s needs, he would like to see energy loads distributed to only sections of the house in use, as well as the ability for clients to control how energy is used throughout the home (on site and from satellite locations). Cottage Home sees one challenge to moving forward with these ideas is getting sub-contractors to approach basic air sealing, insulation, proper HVAC sizing, and design aesthetics with an effective mindset. Cottage Home has established themselves as innovators and leaders in the design of luxury LEED lake front homes. They continue to partner quality, design and the environment hand in hand to produce sustainability along our beaches.
Quick Numbers – Average HERS Score 51 Average LEED score 75
Learn & see more about their LEED projects below.
2012 IECC Energy Code vs Green Home Certifications
/0 Comments/in Green Home Institute, Illinois, Indiana, LEED Certified, LEED Gold, LEED Platinum, LEED Silver, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Passive House, Tools and Resources, Wisconsin/by Brett Little Many states are in the process of adopting in whole or with modifications the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC). This new code raises the bar in construction design for residential and commercial structures, and as a result, architects / engineers / contractors building to the new code will be affordably offer a choice to their clients for pursuing several above-code certifications such as Energy Star and LEED without too much additional effort or cost.
Many states are in the process of adopting in whole or with modifications the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC). This new code raises the bar in construction design for residential and commercial structures, and as a result, architects / engineers / contractors building to the new code will be affordably offer a choice to their clients for pursuing several above-code certifications such as Energy Star and LEED without too much additional effort or cost.
The new national energy code includes mandatory blower-door testing for building air leakage (less than <3.0 ACH at 50 pascals), which will measure how well contractors have sealed up penetrations between the outdoors and indoor conditioned space. This testing will be required for all projects permitted after the new code goes into effect. Some states have made modifications to the adopted code, such as Illinois which has changed the ACH rate to 5.0 ACH @ 50. View our archived July 12 webinar to learn more about IL Energy Code changes.
Other aspects of the 2012 IECC such as requiring hot water pipe insulation and mechanical ventilation are new items that projects will need to implement. Learn more on a free webinar held Thursday July 12.
So, how do national IECC 2012 requirements relate to voluntary above-code programs like Energy Star, LEED and Passive House? Pretty well actually. has assembled a matrix identifying several energy-related items as written in the code and indicated what the impact or requirements would be in one of these above-code third-party green certification programs. Download national comparison matrix as PDF.
(Illinois-specific modifications are shown in the image below)
What does this mean? Well just by building to the new code, these projects will be very close to meeting the Energy Star for Homes program requirements, and will score very well in programs that require Energy Star version 3 such as LEED or Green Communities. Other green programs that don’t require Energy Star, such as National Green Building Standard or local green home programs will also heavily reward these projects.
LEED for Homes will be requiring Energy Star version 3 beginning at the end of the year, so right now a project can still earn LEED certification by building to Energy Star version 2 requirements which should be easily met on any home that meets IECC 2012.
Take advantage of this sweet spot and earn market recognition by attending a LEED workshop or sign up to earn LEED certification today!
A Green Future in the past – Habitat Registers 100th LEED Home in Grand Rapids
/0 Comments/in Affordable Housing, Gut Rehab, Illinois, Indiana, LEED Gold, LEED Platinum, LEED Silver, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Single-Family Projects, Wisconsin/by Brett LittleAfter dozens of new and gut-rehab LEED projects, the Grand Rapids, Michigan Habitat for Humanity affiliate is ready to begin a new era. That happens to be a really old era too. 
With LEED for Homes-registered project #100, Habitat for Humanity of Kent County will start work on their ambitious “Wealthy Heights” neighborhood effort to rebuild homes built in the 1880’s as affordable, workforce housing. After building one new LEED platinum home (Grand Rapid’s 1st!) and preserving a single-family home and a two-unit in Wealthy Heights over the last couple years, Habitat is ready to start seven more projects this fall. It will also coincide with major road and infrastructure improvements by the City of Grand Rapids. Neighbors in Wealthy Heights get ready for construction season!
“The neighbors and business owners who have led the revitalization effort in this neighborhood over the last three decades made it possible for Habitat to step into the mix. Being historic has been a challenge and a blessing but now become a really desirable location for our home buyer partner families,” said Habitat’s Chris Hall.
As Director of Strategic Initiatives, Hall has been part of this project since 2009 when it was first brought to Habitat. With a history of results, Habitat Kent was in the right place at the right time. “It all happened as we were starting to look at ways to become more effective in transforming entire neighborhoods through our work.”
Since then, Habitat has completed the three home projects but also built a community garden and hosted an AmeriCorps Signature Service Project which offered basic exterior repairs, landscaping and a fresh coat of paint for home owners on Donald Place SE.
“We’ve seen residents show up at hearings in support, out working on site, and they have embraced our new families as part of the neighborhood. For-profit builders are doing work in the neighborhood too. This week I heard from folks as far away as New York City regarding a possible LEED-ND certification. Considering we haven’t even begun the major work yet you’d have to say it’s already been an amazing success story.”
After committing to 100% LEED for Homes certification in 2007, Habitat Kent has gone one to become recognized internationally as a leader in affordable, sustainable design and construction. In fact, they were awarded for “Outstanding Program Commitment” to LEED for Homes at the 2011 Greenbuild Conference and Expo in Toronto.
While the positive energy surrounding this project is building, Hall says there is still opportunity for you to help, “We are always looking for partners—either through financial contributions, donations of materials or professional services, as volunteers on site and even as home buyers.” Anyone can visit habitatkent.org to find out more. “Someone can even gain LEED project experience to use toward a LEED AP credential through Habitat! Anyone interested sustainable design will find something cool about this project.”
Future posts will feature a profile of the 100th registered home at 327 Freyling Place SE as well as the other upcoming and completed projects.
Research is being done by MSU and FSU students and faculty with support from Dow and Habitat. They begin with the lowest cost and simplest forms of energy efficiency including cans of spray foam at joints and in gaps, spray foam in rim joists, and other air sealing measures. From there they will test other wall insulation and mechanical system combinations. At each step the homes are tested and analyzed.
Habitat Director of Strategic Initiatives Chris Hall enjoys seeing young people included in the project, “The Michigan State and Ferris State students have really been on the frontline the whole way and they’re getting their hands dirty—in a good way. What they’re learning will directly be applied to what they do in their careers in architecture, engineering, construction management or beyond. And that their work on these homes specifically will benefit a low-income family is especially cool.”
More details on the research project https://greenhomeinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/06/Black-Hills-Home-Energy-Research-Project-Habitat-for-Humanity-Kent-County-.pdf
Want to learn more about affordable Green/LEED major rehabs to existing homes? Free recorded webinar on Habitat’s success here https://www.fuzemeeting.com/replay_meeting/50e23e6d/2385117 Need CEUs for watching this? Email us Info@allianceES.org
Menu
GreenHome Institute
GreenHome Institute
ATTN José Reyna
1451 Lake Drive SE, #6484
Grand Rapids, MI 49516
Tel: (616) 458-6733
Email: info@greenhomeinstitute.org
About Us
Recent Posts
- April 2024 GreenHome and Sustainability Jobs Round-Up.
- Protected: Public comment on Inflation Reduction Act Home Rebates opening in MI and beyond
- Shawn Neinhouse completed Certified GreenHome Professional Training
- Please take this MSU Student’s Mass Timber Survey
- Clean Energy Credit Union Clean Energy For All Reduces Barriers