The Sustainable House. LEED Platinum
The Sustainable House is one of the worlds’ highest ranked and highest rated home for: LEED for Homes®, Energy Star® and Minnesota GreenStar® programs. It is incorporates a Permaculture designed landscape, utilizes a Xeriscape criteria for landscaping, it utilizes the criteria for Century Design Shelters, American Lung Association healthy home criteria, Universal Living criteria and Smart House criteria. This 1948 remodel in Minnetonka, Minnesota, USA was created by 7 teams of 248 individuals in 2007 and 2008.
 View & Download Project Profile PDF
View & Download Project Profile PDF
The House Basics
In order to achieve LEED Platinum status, Live Green Live Smart/The Sustainable House™ must meet a rigorous set of guidelines that require exceptional attention and innovation on the part of the builders and designers.
Sustainable Energy Systems
The most conspicuous innovations are in the ways the House actively uses (or doesn’t use) energy. Because this is a demonstration project, the House incorporates many redundant energy supplies – it is important for us to show how not just one, but many, systems work and how they work side-by-side.
- Solar panels provide both electricity for the home and energy to heat water.
- The Honda/Climate Energy Freewatt™ “combined heat and power” (CHP) system provides, via a generator and furnace run on natural gas, co-generating electricity and forced-air heat.
- Underneath the House’s front walkway are four 135-foot-deep geothermal wells, which circulate a non-toxic solution through pipes to capture the stable temperatures beneath the surface. The energy of the Earth’s heat is transferred to a WaterFurnace™, which can heat the home in the winter and provide air conditioning in the summer.
Environmentally-Conscious Applications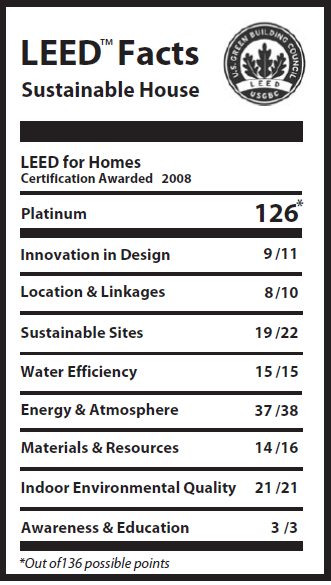
The green building materials and techniques as applied to the House are less conspicuous than alternative energy sources, but no less important to our Platinum remodel.
- Efficient insulation and an air transfer system ensure that none of the heat or cold generated goes to waste, and that the air inside the home stays clean and breathable.
- Solatubes provide natural sunlight all day long, even in the basement, reducing electricity needs.
- Every lightbulb in the house is an energy-efficient compact fluorescent or LED.
- Low-voltage radiant in-floor heating is an efficient way to reduce furnace needs.
- Greywater is collected from the showers for reuse in the double-flush toilets.
- Windows are triple-glazed and argon-filled to reduce heat transfer.
- Appliances are EnergyStar rated, and an induction stove is used for cooking.
- All electrical energy purchased from the grid is the product of windfarming – no coal-fueled energy will be used in the House.
Conservation and Pollution Control
Remodeling an existing home instead of building a new one allows us to keep our construction footprint to a minimum. Remodeling when more usable living space is needed also preserves untouched land, reducing the land and resources needed for specific construction.
- To rebuild the home we have reused as many of the original components as possible – including the 2×6 studs reused to extend the eaves out from the house to save energy needed for cooling, and to protect sidewalls and windows from Minnesota’s weather extremes.
- Anything that cannot be reused is recycled – such as the House’s old stucco – and anything that cannot be recycled is handled by responsible disposal to reduce pollution of air, soil, and water.
- Studs for the new additions (foyer and garage) are 2×4 instead of the standard 2×6. They are also spaced farther apart – 24 inches on center – providing about a 30% savings in new lumber used.
- Most new wood is FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certified to come from sustainable forests.
- Furniture, cabinetry, and countertops are made with recycled or sustainably-harvested materials, and are free of harmful chemicals.
- Paints and varnishes are free of harmful VOCs (volatile organic compounds) and formaldehyde.
- The highly efficient insulation is no-VOC, and an energy heel enclosed in an interior soffit minimizes cold and hot air import by protecting the jointure of walls and roofline.
- Foundation concrete is made with 40% fly ash – recycled sooty waste from coal plants – which is less expensive and more durable than a standard Portland cement mixture.
- Potable water from municipal supply is further filtered with a purification system.
- Water-saving devices include automatic on-off faucets, the batteries of which are recharged by water flow through the supply valves, and double-flush toilets that flush once for liquids and twice for solid waste.
Land Management
In meeting conservation and efficiency requirements, what goes on outside the House is equally as important as what goes on inside the House.
- Rain gardens planted with native plants collect rainwater and allow percolation back into the ground instead of runoff into storm drains. Cisterns collect additional rainwater from the roof and gutters of the House – a two-inch rainfall provides a month of plant and lawn watering.
- Native plants requiring less water are established, with an emphasis on those especially suited for the local climate and the House’s particular site.
- Reduction of turf grass area means a reduction in lawn maintenance needs.
- Behind the house a permaculture microclimate and intensive garden allow the homeowners to grow and enjoy their own fruits and vegetables.
- Hardscapes are paved with permeable materials to reduce run-off into storm sewers and waterways.
More Details and project journal can be found here
http://livegreenlivesmart.org/shelter/sustainable_house/default.aspx













Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!