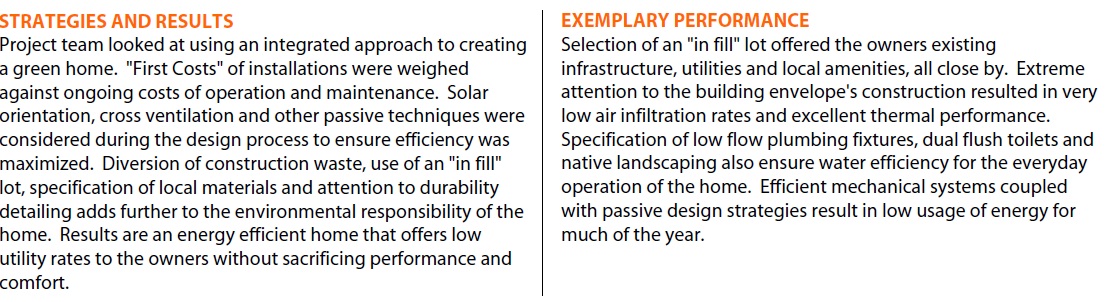
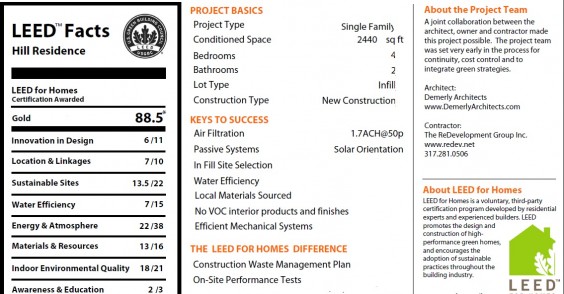
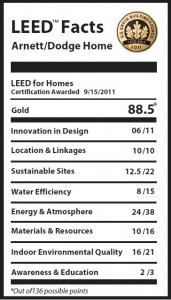
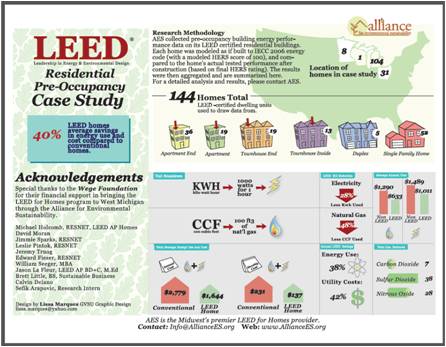
Imagine that every building maintained the ecological balance needed to sustain life on earth. Then, imagine all of humanity motivated to take action, to make this dream a reality. An immensely complicated goal? Maybe. But if we put our fears of failure at the back of the bus, we will maximize the possibility of success.
View & Download Project Profile Here
An immensely complicated goal? Maybe. But if we put our fears of failure at the back of the bus, we will maximize the possibility of success.
Nature has provided us with many examples of “buildings” that achieve an ecological balance. If we follow her example, it is indeed realistic to believe we can prevail.
An Ecologically Balanced Building (EBB), then, is the most advanced building possible for our times 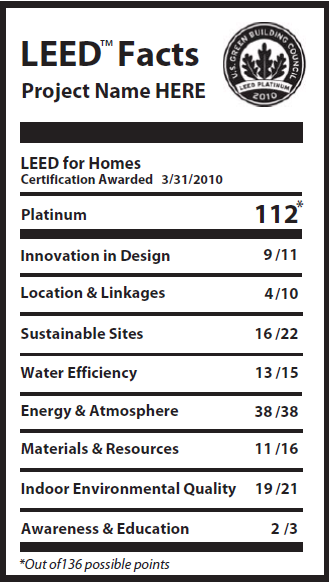 because it strives to replicate the ecological balance found in nature.
because it strives to replicate the ecological balance found in nature.
An EBB incorporates a multitude of interrelated, smart design choices, resulting in a building that virtually lives and breathes, is beautifully balanced, aesthetically pleasing, and is socially responsible and sustainable. It must meet the following criteria:
1. Generate more clean energy than it uses.
2. Sustainably manage the use of water.
3. Waste nothing.
4. Adapt to new conditions.
5. Work symbiotically with all other living things.
6. Eliminate toxins and pollutants.
7. Add beauty & justice to our world
We have the technology and the building science to achieve these lofty imperatives. Fortunately, we are also able to monitor, measure, and verify claims that a building actually accomplishes its intended goals. If we can’t prove our claims, they are meaningless.
The Isabella EBB Project’s initial goal was to create the most environmentally conscious building possible. It targeted integrating all seven design criteria listed above. Additionally, each criterion is monitored, measured and verified to prove, we can indeed live in balance with nature. Following is a description of how the Isabella EBB Project integrated the design criteria:
1. The Isabella EBB Project was designed to consume an annual energy load of 4.5 kBTU/sq-ft. It achieved Passive House Certification, (HERS rating of 3), as the design method to achieve this extremely low energy use index. This is similar to having a 200 MPG car in lieu of our standard a 25 MPG car. There are 9,700 Heating Degree Days in this climate zone & 189 Cooling Degree Days. This was accomplished through the design and construction of thermally broken/R 55 walls and R 90 roof, the use of high performance windows with glazing selected specifically to optimize the solar gain for each orientation and an air tightness of .5 air changes per hour. Using BTU meters on the heating distribution system, the system is to telling us if the design loads are being met.
2. Because extreme measures were taken to reduce the energy loads for this building, renewable energy generation produces more energy than is needed to operate the building. An 11,000 kWH per year PV system/8.4 kw peak load and 92 solar heat collecting vacuum tubes averaging 172,500 BTUs per day collect renewable energy. An experimental long term solar storage area using 16 inches of EPS insulation on all six sides contains both waste taconite from mines and sand. Excess solar heat collection in the summer, fall and spring are stored in this solar storage containment area under the building. The monitoriong system is gathering temperatures of the containment area, the Kwh generated and used and kBTUs for the collection system. We hope to prove that we are producing more clean energy than we use and that this solar storage system can be scaled down for use in other buildings.

3. Two additional areas used for solar storage: a 500 gallon water tank and an 80 gallon domestic hot water tank. These are also being monitor and measured to tell us how hot they are and how many days of cloudy conditions depletes the stored energy supply.
4. A small electric boiler is used for backup energy should the building need it due to depletion of solar energy. This boiler is also being monitor to tell us if it is being powered on. This has already proven to be a great diagnostic tool, as it told us that the relays and sensors were not properly sequenced because the boiler was turning on whenever the domestic hot water dropped a few degrees.
5. A Heat Recovery Ventilation System makes sure that the building and occupants are receiving the right amount of fresh air at the right temperature. An innovative ground loop heat recovery system is connected to the HRV to preheat the outside air prior to being heated by the exhaust air from the building. The success of preheating the incoming sub zero temperature fresh air with heated water from the ground near the footings of the building is being gathered by the monitoring system. We hope to discover a 10 to 15 degree preheating of temperature through this system.
6. A rain water collection system and vegetative roof assures that water continues to perform its job of replenishing the aquifers and supporting plants and animals that conversely support an ecologically balanced building.
7. Information being stored through the use of the monitoring system is allowing the building to be adapted to new conditions and future improvements. Security alarms, for example, are sent when power, pumps, temperatures or water levels are not performing as intended. Historical data gives us the ability to adjust and improve the performance due to accessibility to baseline and historical data.
8. An extreme waste and material management system was incorporated in this EBB. Sustainable & reclaimed wood products, fast growing bio-fiber products, repurposed materials (e.g., old doors for ceilings, old radiators fins for guard rails, old wine barrels for chairs, old chalk boards for sills, and reclaimed tile), contribute to achieving zero waste and low life cycle assessment values.
9. Two highly recognized environmental third party auditing/certifications (LEED and Passive House) were achieved for this project, certifying the project at it the highest level possible. This achievement summarizes that there were many other features, to lengthy to describe for this entry, that make this project one of the most advanced ecologically balanced buildings of our times.
10. Social justice and beauty are parts of ecology that acknowledge the value of spiritually engaging people through art while also supporting the notion of providing equal access and opportunities to all people. The Isabella EBB project embraced adding beauty through the creation of a place that is welcoming, educational, inspiring, healthful, intriguing and fun. The importance of social justice was a goal that surfaced during the learning experiences of the project. Consequently, the project will be willed to the Wolf Ridge Environmental Learning Center, as an extension of their educational mission of teaching and influencing students the importance of living in balance with nature.
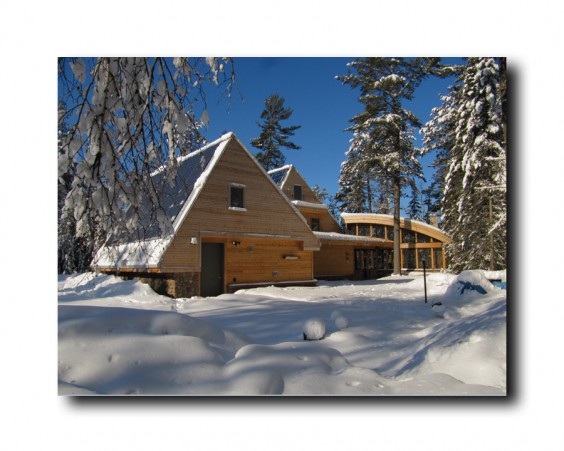

Isabella EBB Project Team
The critical success factors for the project team included:
1. keeping the integrated design process alive and well throughout the entire projects development,
2. checking boiler plate designs at the door,
3. if the project team achieved the goals stated above the points would follow and certification would provide the auditing needed to further validate our assumptions.
3. understanding that everyone was on a ecological educational journey
4. that fearless, open and honest communication was mandatory, (typical passive/aggressive northern climate personality styles would keep innovation from reaching its potential).
Owner: John Eckfeldt eckfe001@umn.edu
Architect/Owner: Nancy Schultz, AIA LEED AP, nschultz@compassrose-inc.com
Energy Conservation Specialist: Mikeal LeBeau, Conservation Technologies, Inc. mlebeau@conservtech.com
Builder: Brad Holmes, Rod and Sons Carpentry, mooshed2@msn.com
Electrician/Designer: Justin Bartuss, voltage@q.com
Mechanical Engineer: Bill Gausman PE, Monitoring and Verification System, bill.gausman@peopleselectric.com
HVAC & Plumbing Contractor: John Hill, Heating Plus, heatplus@frontiernet.net
Landscape Architect: Gus Blumer, SEH, gblumer@sehinc.com
Green Rater: Jimmie Sparks, The Neighborhood Energy Connection, jimmie@thenec.com
LEED Provider: Mike Holcomb, Green Home Institute, mike@homeinspectorgeneral.com