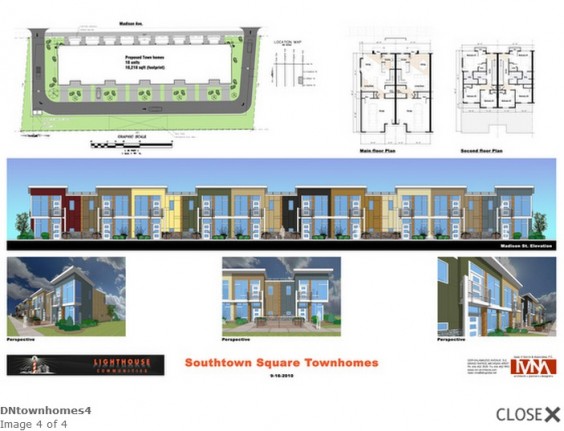
Nine new LEED for Homes registered townhomes in Southeast Grand Rapids are under construction as the first leg of a much larger proposed project by LINC Community Revitalization, Inc. to replace abandoned foreclosed homes with modern, energy efficient townhomes.

The project, Southtown Square, demolished two dilapidated townhouses and a vacant commercial printing business and remediated contaminated soil. Now, nine affordable-rate townhomes are heading for completion, part of a project that could replace some 20 foreclosed properties with 41 modern homes in a neighborhood where many families have struggled to keep their homes, and lost.
The nine two-story townhomes (537 and 539 Hall St. SE; 454 and 456 Umatilla St. SE; 429, 431 and 433 Umatilla St. SE; and 428 and 430 Woodlawn St. SE) will run 800 to 1,150 square feet. Most offer three bedrooms and two-and-a-half baths, says Stephanie Gingeritch, LINC real estate development director. All of them will have full appliance packages and in-home laundry. One home will have a handicap accessible main floor bathroom and bedroom.
LINC purchased the properties from the Michigan Land Bank, Gingeritch says. Work on another two-building townhouse project near Hall and Madison Avenue SE begins in September.
“This is part of a larger redevelopment project where we will be purchasing additional foreclosed townhouses from the State of Michigan and redeveloping those as affordable units,” Gingeritch says. “We recently submitted an application for tax credit financing for an additional 41 units of housing (five additional sites, 20 buildings) on Umatilla and Gilbert. We’ll hear in March 2013 if that is awarded.

“We’re glad we can bring this quality development to the neighborhood where there are already families who are established and don’t have to move out of the neighborhood to have this,” Gingeritch says.
The project is part of the Neighborhood Stabilization Program 2 to stabilize neighborhoods damaged by the economic effects of properties that have been foreclosed upon and abandoned.
Architect: Isaac V. Norris & Associates, P.C.
Construction: Orion II Construction Inc.
Source: Stephanie Gingeritch, LINC Community Revitalization, Inc.
Writer: Deborah Johnson Wood, Development News Editor