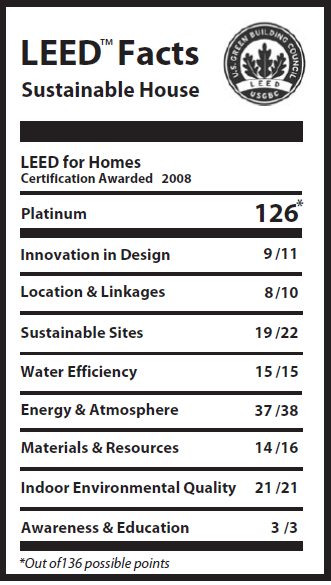
The total cost was $1.6 million. That may seem like a lot of money, but if you look at any other custom-built house this big—it’s 2,675 square feet on a double lot in Chicago—it’s going to cost at least that much. Incidentally, the green materials generally were no more expensive than conventional alternatives.
ELLE DECOR: Why did you decide to build a LEED platinum house?
MICHAEL YANNELL: I wanted to set an example. I had been very frustrated with the construction I was seeing in Chicago. There are so many green options, but nobody was using them. People assume it’s too cold, it’s too cloudy, for solar energy. I wanted to show it could be done here.
ED: So it’s a kind of demonstration house?
MY: I’m not saying every house should be like mine. I’m saying, look at my house, take one detail, and start there.
ED: To accomplish that, you have to be willing to let the world see how you live.
MY: After I moved in I began giving tours constantly—usually an hour long, and limited to ten people, because there were always lots of questions. We started outside the house, and I explained the macro design of the home and then went room by room. I think people have been surprised by how beautiful the house is on the inside. I don’t know what they were expecting.
ED: So, give us the tour.
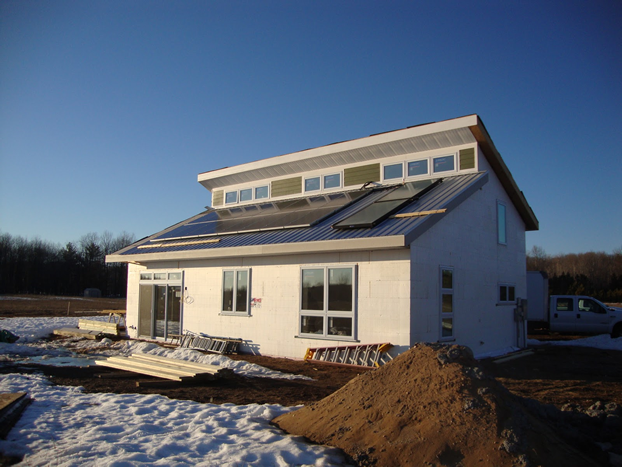
MY: The house is divided into two wings, so every room has a southern exposure. I think that’s a huge benefit, to not have any room be always dark. I never have to turn a light on during the day. In the winter months, it really has a beneficial psychological effect. The north side, by contrast, has only a few small windows—you’d lose too much heat otherwise.
ED: The solar panels all face south.
MY: Yes. But it doesn’t jump out as a house with solar tacked onto it. One of the things the architects insisted on was having as many of the solar panels hidden from view as possible. That’s one of the reasons the roof has that V shape. All the panels are on the north side of the V, and the south side of the V hides them from sight.
ED: How much did all this cost?
MY: The total cost was $1.6 million. That may seem like a lot of money, but if you look at any other custom-built house this big—it’s 2,675 square feet on a double lot in Chicago—it’s going to cost at least that much. Incidentally, the green materials generally were no more expensive than conventional alternatives. The big items were the heating and cooling systems. But you can take tax credits for 30 percent of those. So basically I won’t owe income tax for the next few years.
ED: How did you choose the finishes?
MY: Every material that went into the house has some environmental story. The exterior is a combination of durable fiber-cement board and Forest Stewardship Council–certified cedar, covered in a cocoa soy-based stain. I love the contrast of dark and light.
ED: And the interior finishes?
MY: In the south wing the floors are a dark brown recycled-porcelain tile, which is very earthy, very soft. In the north wing the floors are made from scrap lumber, which would have ended up in a landfill. It’s walnut, with a clear coat that gives it a warm, natural feel. In the bedrooms, I chose dyed-clay walls. Besides looking good, they absorb sound better than regular painted walls. And clay also absorbs humidity, which is a nice feature in the summer.
ED: Does the furniture have the same kind of environmental credibility?
MY: Much of it is steel, which is recyclable. That’s one of the reasons we bought a lot of furniture from Knoll. The house has a midcentury look, so Knoll was right up our alley. All of the fabrics are Greenguard certified.
ED: What about the art?
MY: We chose the work of a Venezuelan artist, Radames, who works with Plexiglas scraps. I liked the designs, but I don’t like Plexiglas, because it has a high petroleum content. So we asked if he could work with 3form, which is an eco-resin product. He came up with seven or eight pieces for inside and a sculpture for the backyard, so it’s a green art collection as well.
ED: Speaking of art, the house has gallery reveals—those subtle recesses where the walls meet the windows and door frames.
MY: We used reveals throughout the house. I had never even heard the term before. It became known as the “R-word” during the design phase. It added to the cost, but it was really important to the architects. I have to admit, I appreciate how good it looks.
What the Pros Know
Architect Jonathan Boyer, of Chicago’s Farr Assoc., says the house is designed to produce as much energy as it consumes. But, he adds, he knew it would get the point across only if it also looked good.
• Be flexible: Most of the materials were produced locally—a key green principle—but when he needed an attractive cement board, Boyer had to buy a European product.
• Do double duty: The butterfly roof provides shading in summer and optimal placement for the solar panels. The V shape collects rainwater, which is used for irrigation.
• Exploit technology: “Thanks to LEDs, we were able to flood the rooms with light,” says Boyer, “despite using fixtures so compact you hardly see them.”
Click here to see the gallery of the Home
Written by Fred A. Bernstein • Photographed by Tony Soluri • Produced By Susan Victoria